

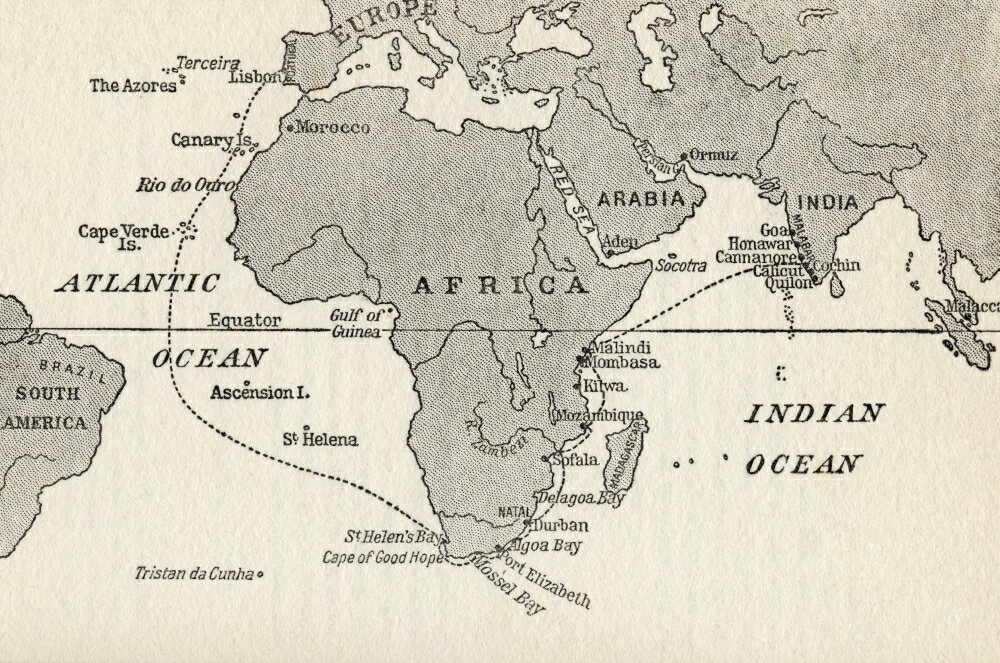
The violence and hostage taking employed by da Gama and those who followed also assigned a brutal reputation to the Portuguese among India's indigenous kingdoms that would set the pattern for western colonialism in the Age of Exploration. Da Gama's discovery of the sea route to India opened the way for an age of global imperialism and enabled the Portuguese to establish a long-lasting colonial empire along the way from Africa to Asia. This is widely considered a milestone in world history, as it marked the beginning of a sea-based phase of global multiculturalism. His initial voyage to India by way of Cape of Good Hope (1497–1499) was the first to link Europe and Asia by an ocean route, connecting the Atlantic and the Indian oceans and therefore, the West and the Orient. 1460s – 24 December 1524), was a Portuguese explorer and the first European to reach India by sea. All rights reserved.Vasco da Gama, 1st Count of Vidigueira ( c. Copyright © 2023, Columbia University Press.
The Columbia Electronic Encyclopedia, 6th ed.
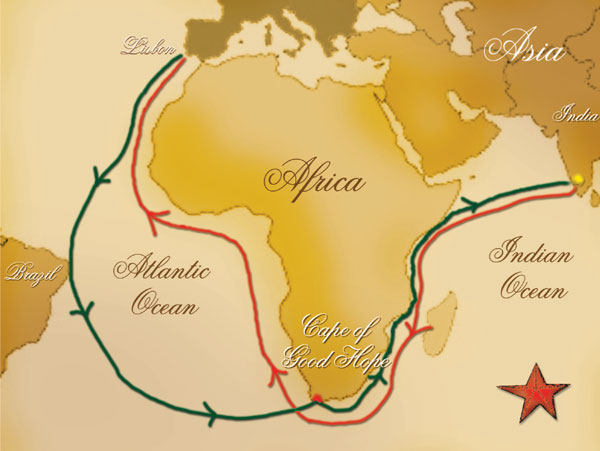
Cliff, Holy War: How Vasco da Gama's Epic Voyages Turned the Tide in a Centuries-Old Clash of Civilizations (2011) and The Last Crusade: The Epic Voyages of Vasco Da Gama (2012). Hart, Sea Route to the Indies (1950, repr. Jayne, Vasco da Gama and His Successors (1910, repr. Corrêa, The Three Voyages of Vasco da Gama and His Viceroyalty (1869, repr. See A Journal of the First Voyage of Vasco da Gama (1898), the journal of one of Gama's subordinates G. Gama's voyage is the subject of Camões's epic The Lusiads. In 1524 he was sent back to India as viceroy, but he died soon after his arrival. He was harsh in his methods and was not as good an administrator as many of the Portuguese captains who later went to the East, but he was the first, and he was honored with many tributes and the title of count of Vidigueria. With this force he attempted to establish Portuguese power in Indian waters and sought to secure the submission of a number of chiefs on the African coast. Gama dictated the instructions for Cabral's voyage (1500–1502) to India, and in 1502 he himself led a fleet of 20 ships on his second India voyage. This voyage opened up a way for Europe to reach the wealth of the Indies, and immediately Portugal gained great riches from the spice trade out of it ultimately grew the Portuguese Empire. With four vessels, he rounded the Cape of Good Hope, passed the easternmost point reached by Bartolomeu Dias in 1488, continued up the east coast of Africa to Malindi, and sailed across the uncharted Indian Ocean to Calicut. His epochal voyage (1497–99) was made at the order of Manuel I. väsh´kō dä gä´mə, c.1469–1524, Portuguese navigator, the first European to journey by sea to India.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
